Zirconium Oxide (ZrO₂)
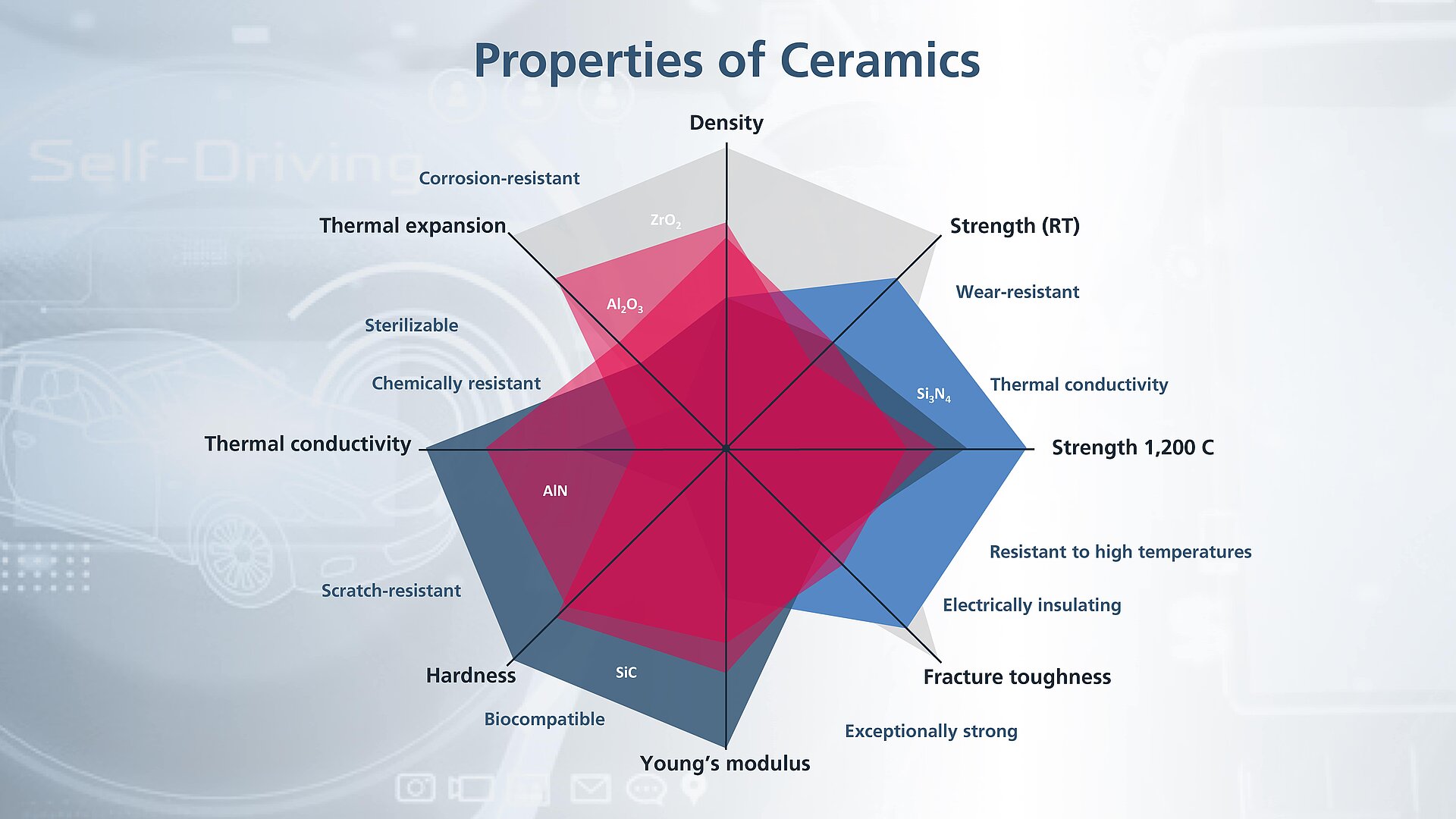
Unlike other ceramic materials, zirconium oxide (ZrO2 –also known as zirconia) is a material with very high resistance to crack propagation. Zirconium oxide ceramics also have very high thermal expansion and are therefore often the material of choice for joining ceramics and steel.
Another outstanding property combination is the very low thermal conductivity and high strength. In addition, some types of zirconium oxide ceramics can conduct oxygen ions. Components made from this material are significantly more expensive than components made of alumina ceramics.
Application Examples
Due to their biocompatibility, zirconium oxide ceramics are used, for example, as a material for crowns and bridges in the dental industry, as tools for wire forming, as an aid in welding processes, as technical cutters in the textile industry, as an insulating ring in thermal processes and as an oxygen measuring cell in lambda sensors. Other fields of application include electronics, aviation and energy generation, where zirconium oxide is used as an insulator and in high-performance components.
In the future, the material could play a key role in environmental and energy technology, e.g. in fuel cells, which rely on durable and stable materials.
Properties of Zirconium Oxide (ZrO₂)
- High thermal expansion (α=11 x 10-6/K, similar to some types of steel)
- Excellent thermal insulation/low thermal conductivity (2.5 to 3 W/mK)
- Very high resistance to crack propagation, high fracture toughness (6.5 to 8 MPam1/2)
- Ability to conduct oxygen ions (used for the measurement of oxygen partial pressures in lambda probes)